As technology continues to revolutionize every facet of life, a pressing challenge has emerged: balancing innovation with the well-being of users. In the age of digital addiction, ethical engineering is not just a lofty ideal; it is an urgent necessity. With countless people experiencing adverse effects from excessive device use, engineers and designers must now grapple with the responsibility of creating technologies that foster progress without compromising mental health.
The Rise of Digital Addiction
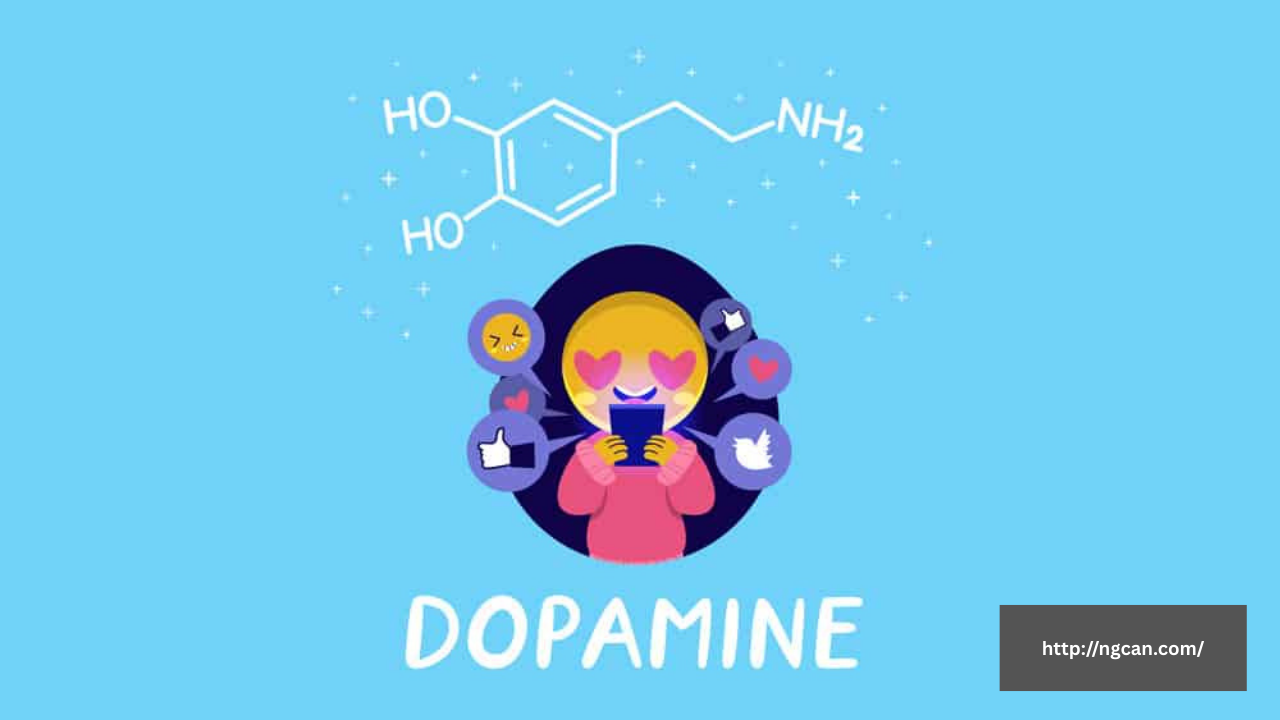
Digital addiction refers to the compulsive use of digital devices, apps, and platforms, often to the detriment of an individual’s emotional, social, and physical well-being. Features like infinite scroll, algorithmic content recommendations, and constant notifications have been designed to maximize user engagement—and profits—but they also contribute to prolonged screen time and addictive behaviors.
Studies have linked digital addiction to rising levels of anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, and reduced attention spans. As the negative consequences become more evident, society is demanding that tech creators address the unintended harm caused by their innovations.
The Role of Ethical Engineering
Ethical engineering is the practice of designing technology that prioritizes human values, health, and dignity alongside functionality and efficiency. It demands that engineers, developers, and designers critically assess the broader impact of their creations on individuals and communities.
In an environment where success is often measured by user engagement metrics and growth curves, ethical engineering challenges these traditional markers. Instead of asking, “How can we keep users engaged longer?” engineers must now consider, “How can we serve users’ best interests?”
Principles for Ethical Engineering
- Design for Empowerment, Not Exploitation
Ethical engineering emphasizes giving users control over their interactions with technology. This includes options to customize notification settings, set time limits, and track usage patterns. Empowering users fosters healthier relationships with technology. - Transparency and Informed Consent
Users should be fully aware of how their data is collected, how algorithms influence their experience, and the potential psychological effects of using a product. Transparent communication builds trust and allows users to make informed choices. - Incorporating Well-being Metrics
Rather than focusing solely on engagement or revenue, tech companies should track metrics related to user satisfaction, digital well-being, and life enhancement. Measuring success by positive impact shifts priorities toward ethical outcomes. - Promoting Mindful Design
Mindful design integrates natural stopping points, encourages breaks, and avoids manipulative features that hijack attention. Designing for mindfulness helps users develop healthier tech habits and improves overall user satisfaction. - Ethical AI and Algorithm Development
Engineers must ensure that AI systems promote balanced content consumption rather than reinforcing addictive loops. Ethically trained algorithms can recommend diverse, meaningful content rather than focusing purely on maximizing clicks.
Moving Forward
Balancing progress and well-being is a complex challenge but not an impossible one. Engineers, tech companies, and policymakers must collaborate to embed ethical considerations into every stage of technology development. Industry leaders must invest in research on digital health and integrate findings into product design.
Ultimately, ethical engineering in the age of digital addiction means putting people first—creating technology that enhances lives rather than diminishes them. By embracing this mission, the tech industry can drive innovation that not only shapes the future but also safeguards the humanity of its users.